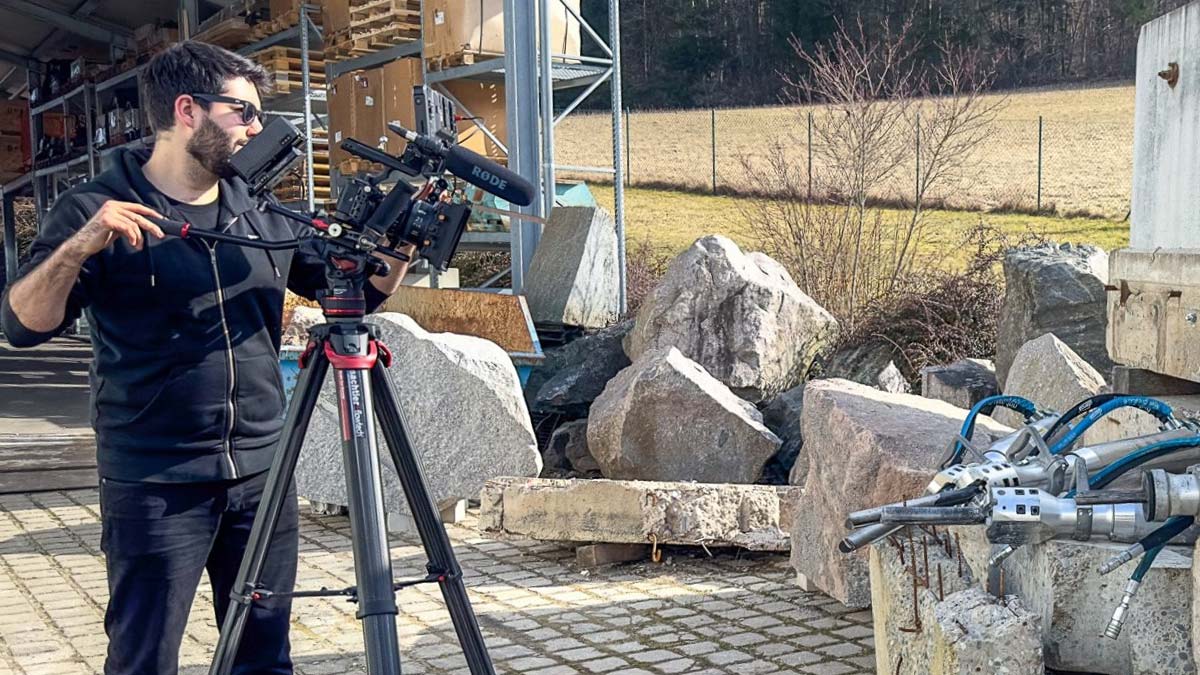
The repurposing of a structure—often also referred to as change of use, revitalization, or reclassification—unlocks new functions for existing buildings. Whether an industrial hall becomes a training center, a parking garage becomes a logistics hub, or an office building becomes housing: Successful projects combine precise assessment of the existing asset, careful interventions in the load-bearing structure, and a material-efficient construction approach. Crucial are controlled deconstruction and adaptation measures, such as creating openings, removing structural elements, or selectively stripping out built-ins. In many cases, concrete demolition shears as well as rock and concrete splitters from Darda GmbH are used, supported by hydraulic power packs and—depending on the component—combination shears, steel shears, multi cutters, or tank cutters. This enables low vibration levels, precise, and component-friendly interventions—a plus for the structure, the neighborhood, and the schedule.
Definition: What is meant by repurposing of structure
Repurposing of a structure means the change of use of an existing building or civil engineering structure, including all structural, technical, and organizational measures required for it. This includes adapting the load-bearing structure, reorganizing floor plans, installing shafts and openings, renewing building services, and the selective deconstruction of components that are no longer needed. The goal is to continue using the existing asset in a resource-efficient manner, extend its service life, and reliably meet the requirements of the new use (e.g., fire protection, accessibility, acoustics, vibration behavior, loads). In this context, controlled demolition and cutting methods—particularly with concrete demolition shears and rock or concrete splitters—play a key role.
Core tasks and typical work steps in repurposing
Repurposing follows a structured process from survey to commissioning. Key steps are: capturing and evaluating the existing condition (structure, materials, hazardous substances), concept development and verification, selective deconstruction and strip-out, openings and breakthroughs, strengthening and upgrading measures, fit-out and building services, quality assurance and documentation. During the selective deconstruction phase—depending on member thickness, degree of reinforcement, accessibility, and vibration tolerance—concrete demolition shears or rock and concrete splitters from Darda GmbH are often used, supported by hydraulic power packs. For steel components, vessels, or piping, steel shears, multi cutters, combination shears, or tank cutters are suitable. This categorization facilitates the choice of the appropriate method across the application areas of concrete demolition and special demolition, strip-out and cutting, as well as special operations.
Requirements and boundary conditions of a change of use
Repurposing must be properly prepared in technical and organizational terms. This includes coordination with the responsible authorities, compliance with relevant standards, and consideration of load-bearing capacity, fire protection, sound insulation, energy efficiency, occupational safety, and construction processes in existing buildings. Concrete requirements depend on the location and project; it is advisable to clarify these at an early stage for each project and to base the technical verifications on robust as-built data.
Regulatory and organizational aspects
Approval processes, verification obligations, and stakeholders (for example for structural safety, fire and emissions protection) vary by country and region. Project teams should clarify early which documents are required and how interventions in the existing fabric—such as vibrations, dust, noise—can be organized operationally so that neighbors are protected. Low-vibration methods with concrete demolition shears and rock and concrete splitters make this coordination easier, especially in sensitive settings.
Heritage conservation and existing value
For heritage-worthy structures, conserving the fabric and using deconstruction-friendly methods take priority. Targeted interventions, minimal edge cracking zones, and precise material separation support a careful implementation. Splitting methods and the controlled size reduction of concrete members with concrete demolition shears help protect historic surfaces and adjacent elements.
Survey and diagnosis of the structure
Sound planning is based on reliable data. In addition to drawings and reports, exploratory openings and material tests are required to identify reserve capacity and weak points. The choice of opening method influences the quality of the findings: low-vibration and low-dust methods improve the significance of investigations and reduce collateral damage.
Structural analysis and material condition
Key information includes rebar location, concrete cover, cracks, concrete carbonation, chloride contamination, and cross-sectional reserves. For exploratory openings and exposure, small, controlled interventions are suitable: With concrete demolition shears, samples can be gently extracted from reinforced concrete; rock and concrete splitters can open massive members along defined lines without large-scale vibrations.
Hazardous substances and the construction material cycle
If hazardous substances are suspected, qualified investigations are necessary. Selective deconstruction and clean separation by type facilitate recycling. Tool selection and work sequence should aim for low cross-contamination and clean cut edges—an advantage of precise cutting and splitting techniques.
Selective deconstruction and strip-out as the basis for repurposing
Strip-out and controlled deconstruction create space for new floor plans, installations, and load paths. The goal is to remove only what is necessary and to influence the structure in a targeted way—with as little noise, dust, and vibration as possible.
- Separation of non-load-bearing layers and built-ins
- Creating openings for doors, lifts, stairs, and shafts
- Deconstruction of local strengthening, balcony slabs, downstand beams, or bearing areas
- Dismantling of steel sections, plant components, vessels, and pipelines
Tools and methods for low-vibration work
Concrete demolition shears enable controlled removal and size reduction of reinforced concrete members—suitable for interiors, sensitive existing structures, and dense urban settings. Rock and concrete splitters generate defined separation cracks in concrete or natural stone and are ideal for massive cross-sections, pile heads, and members with stringent vibration and noise requirements. Hydraulic power packs supply the tools efficiently, even where access is limited. For hybrid constructions, combination shears are suitable, while multi cutters and steel shears cut reinforcement, sections, and plates cleanly. For vessels and large-scale apparatus, tank cutters are used. These methods are typical for the application areas concrete demolition and special demolition, strip-out and cutting, as well as special operations.
Producing openings and breakthroughs with precision
Openings in slabs and walls require accurate edges and limited edge damage. Concrete demolition shears allow sectional removal, while splitters direct crack formation—e.g., for elevator shafts or new stair flights. Reinforcement is then cut with steel shears or multi cutters. This interplay increases dimensional accuracy and minimizes rework.
Strengthening the structure and reconfiguring load paths
The new use imposes different requirements on load-bearing capacity, serviceability, and vibration behavior. Common measures include cross-section enlargements, underpinning, additional beams, composite solutions, and local relief. Precise interventions in the existing fabric are crucial.
Interventions in concrete and reinforced concrete members
When removing corbels, upstands, node or connection areas, concrete demolition shears are proven for controlled removal without overstressing adjacent zones. Rock and concrete splitters are suitable for massive member heads where a defined separation plane is required, for example to create new bearing surfaces or joints. Subsequent rebar works can be efficiently prepared with multi cutters.
Steel and composite structures
In steel or composite structures, precise separation cuts are required, for example to remove old strengthening or plant connections. Steel shears and combination shears cut sections and hybrid members in a controlled manner; tank cutters are used for vessels and thick wall sections. In this way, the structure can be prepared for new load paths.
Building services, shafts, and routing
New uses require additional utilities: ventilation, plumbing, electrical, sprinklers. Shafts, slab penetrations, and wall openings should be coordinated with the structure and produced with low vibration. Targeted splitting lines or sectional removal with concrete demolition shears minimize edge cracking and protect nearby service runs and finishes.
Construction logistics, emissions, and occupational safety
Repurposing often takes place during ongoing operations or in dense surroundings. Logistics with short routes, low-dust material handling, and quiet workflows are advantageous. Splitting and shear methods reduce noise and vibrations and make coordination with residents and users easier.
- Set up and encapsulate work areas section by section
- Plan material flows for clean separation by type
- Align equipment selection with emission targets (dust, noise, vibration)
- Continuously review occupational safety and protective measures
Sustainability, resource conservation, and documentation
Reusing components and separating materials by type reduces resource demand. Precise separation techniques support recycling and reduce waste volumes. Clear documentation of interventions—such as location, dimensions, and quality of openings—facilitates later use and facility management.
Special fields of application: tunnels, rock, and industrial facilities
For repurposing infrastructure, underground facilities, or industrial sites, special methods are required. Rock and concrete splitters are proven in rock excavation and tunnel construction when enlargements or new gallery connections are needed. In industrial environments, tank cutters, steel shears, and combination shears enable the safe dismantling of vessels, pipelines, and steel platforms. This allows production areas to be remodeled without affecting the entire structure—a typical special operation.
Project workflow: from idea to commissioning
A consistent workflow secures deadlines and quality: goal definition and feasibility, detailed survey, planning of interventions, selection of methods, trial area or sample opening, step-by-step deconstruction and strengthening, fit-out, and commissioning. In the phases involving interventions in the structure and fit-out, the use of concrete demolition shears and rock or concrete splitters from Darda GmbH has proven effective, complemented by the appropriate hydraulic power packs and cutting tools. This enables openings, partial demolition, and adaptations to be executed in a controlled, asset-friendly manner—the foundation for successful repurposing.