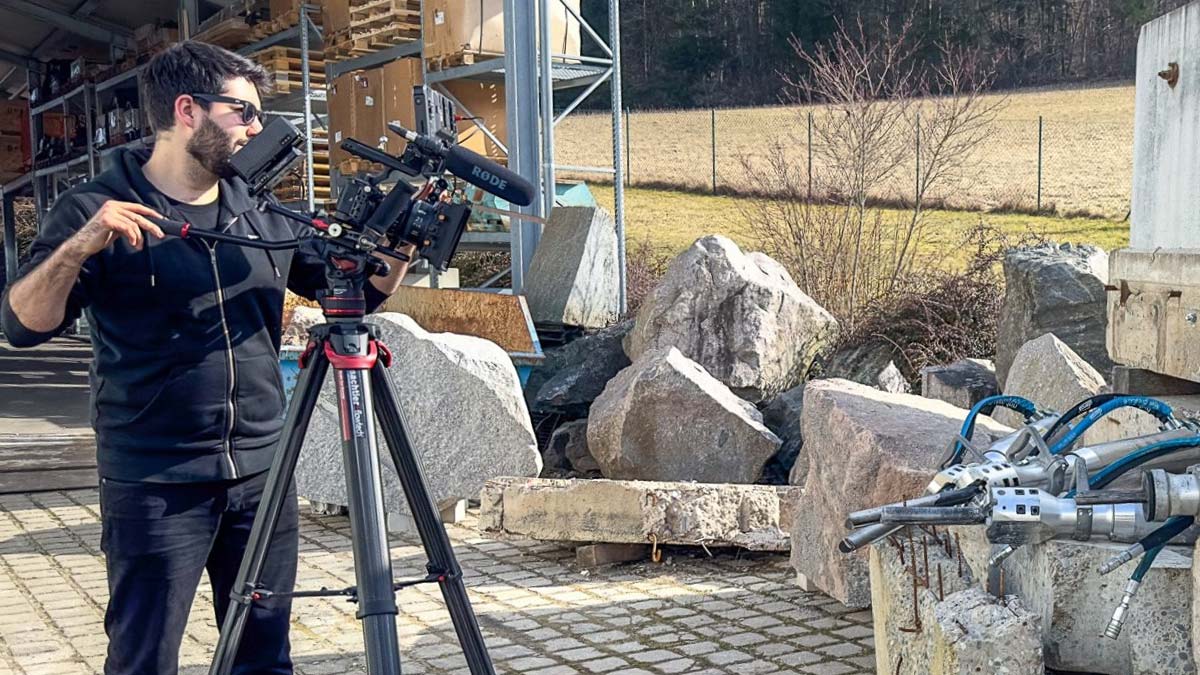
The collapse protection system covers all preventive and accompanying measures that stabilize structures, components, or rock masses in an unstable state so that an uncontrolled collapse is prevented. In practice, the scope ranges from temporary shoring and bracing to controlled separation, through monitoring and orderly deconstruction sequences. Especially in concrete demolition, special demolition, strip-out, rock excavation and tunnel construction, as well as in special deployments, a well-thought-out collapse protection system is the fundamental prerequisite for safety, predictability, and quality. Tools such as concrete demolition shears and rock and concrete splitters from Darda GmbH help steer load paths in a targeted manner, deliberately weaken components, and minimize vibrations.
Definition: What is meant by collapse protection system
The term collapse protection system refers to the systematic identification, assessment, and control of instabilities in structures or rock formations. The goal is to influence load-bearing and bracing elements (e.g., slabs, walls, columns, beams, piers, rock ribs) by means of temporary auxiliary structures, controlled separation methods, and suitable dismantling sequences so that the overall system remains stable. Collapse protection system includes hazard assessment, the establishment of redundant load paths, the removal of peak loads, the limitation of deformations, and monitoring of the construction state. Methods such as low-vibration splitting with stone splitting cylinders, targeted crushing with concrete demolition shears, or cutting steel with multi cutters and steel shears from Darda GmbH help to work on critical interfaces in a controlled and safe way.
Core principles, objectives and fields of application
The collapse protection system follows a few core principles: understand loads, secure load paths, minimize actions, separate components in a controlled manner, monitor changes, and continuously adapt measures. Fields of application range from inner-city deconstruction to strip-out in existing buildings, tunnel construction and rock excavation, all the way to emergency and rescue work. The interplay of planning, temporary auxiliary structures, and suitable equipment technology balances safety, construction progress, and environmental impacts.
Legal framework and recognized rules of practice
The collapse protection system is guided by recognized rules of practice as well as the applicable legal requirements. These include requirements for hazard assessment, qualifications of responsible parties, structural design of temporary states, the safe use of work equipment, and the protection of third parties. These provisions do not prescribe rigid recipes but define protection objectives. Decisive are expert planning, documentation, and supervision of the measures—especially for construction states that deviate from the regular structural system.
Planning the collapse protection system: procedure and responsibilities
A robust concept is developed in several steps under clear responsibility. Darda GmbH addresses the technical implementation with adapted hydraulic systems but remains embedded in an overarching protection concept.
- Survey of existing conditions: geometry, material, damage, cracks, moisture, reinforcement, load transfer, foundation.
- Hazard assessment: failure mechanisms, overturning and buckling risks, progressive collapse chains, vibrations, vibration transmission into adjacent structures.
- Load-path strategy: temporary load transfer, bracing planes, intermediate states, redundancies.
- Choice of measures: shoring, cross-bracing, tie-back anchoring, controlled separation, crushing, splitting, removing additional loads.
- Equipment selection: concrete demolition shears, rock and concrete splitters with matching hydraulic power packs, steel shears, combination shears, multi cutters, tank cutters from Darda GmbH—matched to material, component thickness, and surroundings.
- Sequence and cutting plan: step logic, precautions against buckling/lifting, defined fracture lines, emergency barriers.
- Monitoring: measurement points, threshold values, inspection intervals, documentation, stop rules.
- Spatial organization: access routes, exclusion zones, load-bearing capacity of work areas, crane and equipment logistics.
Temporary shoring and bracing
Shoring secures compression, tension, and bending, while bracing stabilizes out of plane. The objective is a robust intermediate state that safely absorbs work steps and tool forces.
Shoring principles
- Compression members and props take vertical loads; buckling lengths and bearing pressures are decisive.
- Beams, struts, and bracing members provide diaphragm action and limit displacements.
- Tie-back anchoring and tension systems secure against uplift and overturning.
- Bearing surfaces distribute forces; proper seating/preloading and slip prevention are mandatory.
Interaction with the separation method
The shoring must suit the separation and crushing methods used. Hydraulic splitting generates shear and spreading forces; shear operation concentrates crushing and cutting forces. The design of auxiliary structures accounts for these additional loads and limits deformations to defined thresholds.
Load-path management and controlled separation
Controlling loads determines stability. Tools from Darda GmbH help release components without shocklike effects and convert them into manageable segments.
- Rock and concrete splitters with stone splitting cylinders: create defined crack lines, minimize vibrations, and are suitable for massive cross-sections.
- Concrete demolition shears: cut concrete and reduce cross-sections in a controlled way; ideal for removing wall panels, lintels, and edges.
- Steel shears and multi cutters: clean cutting of structural steel, reinforcement, and lines to eliminate restraint forces and hanging points.
- Combination shears: flexible at transition points between concrete and steel.
- Tank cutters: cold-cutting methods reduce ignition sources on vessels and lines; important for collapse and explosion safety.
- Hydraulic power packs: supply the required energy; pressure level, flow rate, and controllability influence process stability.
Collapse protection system in concrete demolition and special demolition
In selective deconstruction the rule is: relieve first, then cut. Concrete demolition shears from Darda GmbH combine gripping, crushing, and cutting, allowing components to be removed section by section. In thick components, hydraulic splitting opens crack paths that dictate load paths and create free edges. The sequence is oriented to global bracing: bracing elements are removed only after alternative load paths have been established.
Typical work steps
- Remove attached loads (coatings, fillings, add-on elements) to reduce weight.
- Install temporary shoring and bracing.
- Prepare defined cut lines using splitting wedges and boreholes.
- Segment with concrete demolition shears and perform controlled lowering/transport.
- Retension and deconstruct step by step, accompanied by instrumented and visual inspections.
Collapse protection system in strip-out and cutting
In existing buildings, strip-out can unintentionally weaken load-bearing elements. Lines, routes, and built-ins often act as unnoticed “links.” With multi cutters, steel shears, and combination shears from Darda GmbH, these connections are separated in a targeted manner before load-bearing components are released. Tank cutters support safe dismantling of vessels and pipelines without introducing additional thermal effects. This keeps the construction state controllable.
Collapse protection system in rock excavation and tunnel construction
In rock and tunnels, stability depends on discontinuities, joints, and water. Rock and concrete splitters from Darda GmbH create controlled split lines with low vibration. This allows loose blocks to be released in a targeted way without weakening the surroundings. Anchors, meshes, and shotcrete are used in parallel. Monitoring deformations and cracks as well as stepwise extraction are core elements of safety.
Natural stone extraction: selective release and edge control
In the extraction of natural stone, the quality of fracture edges is crucial. Hydraulic splitting enables defined joints, reduces hidden micro-damage, and protects adjacent benches. Load shedding takes place via orderly splitting sequences; falling stones are controlled by exclusion zones, catching scaffolds, and retention systems.
Special deployment: incident, fire, earthquake
For acutely unstable structures, time and control are critical. Lightweight hydraulic tools from Darda GmbH enable precise, low-vibration work in tight situations. Priorities are securing access routes, reducing hanging loads, and removing overhangs. Measures proceed step by step, under close observation and with clear abort criteria.
Monitoring and threshold values
Monitoring identifies unstable developments early. Appropriate measurands and simple visual inspections complement each other.
- Crack widths and movements
- Settlements and tilts
- Vibrations and noise levels
- Deformations on shoring and anchors
- Temperature, moisture, water ingress
Practical rules for monitoring
- Define measurement points early, establish reference values, document thresholds.
- Link measurement intervals to construction states (before, during, after individual cutting steps).
- Stop-and-go logic: if thresholds are exceeded, stop work, analyze causes, adapt measures.
Equipment selection: criteria and interfaces
The choice of tools depends on material, component thickness, accessibility, and environmental requirements.
- Concrete demolition shears: for targeted crushing, removal of projections, openings, wall panels; well-suited for controlled segmentation.
- Rock and concrete splitters: for massive cross-sections, low vibration, defined fracture lines; ideal for preparing load-bearing cuts.
- Steel shears and multi cutters: for cutting reinforcement, profiles, beams, and lines to eliminate restraint forces.
- Combination shears: for mixed tasks when concrete and steel interlock directly.
- Tank cutters: when thermal methods are not permitted or ignition hazards must be reduced.
- Hydraulic power packs: power, controllability, and connection concept determine cycle, force, and precision of the process.
Environmental and neighborhood protection
The collapse protection system also protects the neighborhood. Vibrations, noise, and dust affect the stability of adjacent structures. Hydraulic splitting and shear methods reduce vibrations and flyrock compared to percussive methods. Additionally, dust suppression, vibration monitoring, protective walls, and exclusion zones are effective.
Documentation, communication, training
A robust protection concept lives from clear communication and traceable documentation. Responsibilities, measurements, changes in sequence, and releases are recorded. Briefings and training convey the interplay of shoring, cutting, monitoring, and emergency management. Tools from Darda GmbH integrate as building blocks in a holistic safety concept focused on controllability and reproducible work steps.